Your cart is currently empty!
Category: 5th class Evs

Curiosi Quiz Zone: Practice & Improve | “Migration of People”
Class 5 EVS Practice Test – The Curiosi. # Migration of People
Andhra Pradesh | APSCERT

Earth to Space
| Class 5 | EVS Tetbook | Chapter 11
Andhra Pradesh | APSCERT
Home » Solutions » Class 5 » EVS Textbook Solutions » Chapter 11: Earth to Space
Here are the answers to the “Improve Your Learning” section from the lesson “Earth to Space” for Class 5 EVS.
I. Conceptual Understanding
1. What are the differences between latitudes and longitudes?
• Latitudes:
• These are horizontal imaginary lines on the globe.
• They run parallel to the Equator.
• They help in measuring distances north or south of the Equator.
• Longitudes:
• These are vertical imaginary lines on the globe.
• They converge at the poles and are widest at the Equator.
• They help in measuring distances east or west of the Prime Meridian.
2. What do you know about the globe?
• The globe is a miniature model of the Earth.
• It shows continents, oceans, countries, and important geographical locations.
• It helps in understanding latitudes, longitudes, and Earth’s rotation.
• The globe is useful in learning about climate zones, time zones, and different regions of the world.
3. What is the shape of the Earth?
• The Earth is round (spherical) in shape.
• Though the Earth looks flat in small areas, satellite images confirm that it is round.
• Ferdinand Magellan’s voyage around the world proved that the Earth is not flat.
• The shadow of the Earth on the Moon during a lunar eclipse is always circular, further proving its round shape.
II. Questioning and Hypothesis
4. What will happen if the Earth stops its rotation?
• There will be no day and night cycle; one side of the Earth will have continuous daylight and the other side will have continuous darkness.
• Gravity and atmospheric conditions will change, leading to severe natural disasters.
• Oceans and winds will stop moving in their normal patterns, causing climate changes and extreme weather.
• The Earth’s magnetic field may weaken, exposing us to harmful space radiation.
III. Experiments and Field Observations
5. Prepare a model of the solar system and explain it.
• Take balls of different sizes to represent the planets.
• Use a large yellow ball to represent the Sun.
• Arrange the planets in order from the Sun:
• Mercury, Venus, Earth, Mars, Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, Neptune.
• Show the revolution of planets around the Sun using circular paths.
• Explain that planets revolve around the Sun due to gravitational force.
IV. Information Skills and Projects
6. Collect the names of artificial satellites sent by India and write about their purposes.
Satellite Name Year Purpose Aryabhata 1975 India’s first satellite for space research. INSAT Series 1983–present Used for communication and weather forecasting. IRS Series 1988–present Used for Earth observation and resource mapping. Chandrayaan-1 2008 India’s first Moon mission, discovered water on the Moon. Mangalyaan (Mars Orbiter Mission) 2013 India’s first mission to Mars, studied Mars’ surface and atmosphere. Chandrayaan-2 2019 India’s second Moon mission with an orbiter, lander (Vikram), and rover (Pragyan). V. Drawing and Model Making
7. Draw latitudes and longitudes on a ball and explain them.
• Steps:
1. Draw horizontal lines (latitudes) parallel to the Equator.
2. Draw vertical lines (longitudes) from the North Pole to the South Pole.
3. Mark the Prime Meridian (0° longitude) and the Equator (0° latitude).
4. Label important latitudes like Tropic of Cancer, Tropic of Capricorn, Arctic Circle, and Antarctic Circle.
VI. Appreciation, Values, Application to Daily Life, Biodiversity
8. Why is Earth the only habitat for human beings?
• Earth has oxygen and an atmosphere, which are essential for life.
• It has liquid water, necessary for drinking and survival.
• Earth has a moderate temperature that allows humans, animals, and plants to thrive.
• The protective ozone layer shields us from harmful radiation.
• Gravity holds everything in place and makes life possible.
• No other planet in our solar system has these perfect conditions for human survival.
These answers help students understand Earth’s features, space, satellites, and the importance of the planet in supporting life.

Alert Today, Alive Tomorrow
Class 5 | Evs Textbook | Chapter 9
Home » Solutions » Class 5 » EVS Textbook Solutions » Chapter 9: Alert Today, Alive Tomorrow
Here are the answers to the “Improve Your Learning” section from the lesson “Alert Today, Alive Tomorrow” for Class 5 EVS
I. Conceptual Understanding
1. Why should we take safety measures?
• Safety measures help prevent accidents and injuries.
• They ensure that people remain safe in daily activities like traveling, working, and playing.
• Following safety measures protects both individuals and society.
2. What is first aid and when is it needed?
• First aid is the immediate care given to an injured or sick person before medical help arrives.
• It is needed in case of accidents, burns, snake bites, fractures, or any emergency to prevent the condition from worsening.
3. Aparna’s grandfather was bitten by a snake. What kind of first aid is suggested to him?
• Keep the affected person calm and still to slow down the spread of venom.
• Do not try to suck out the venom.
• Tie a cloth or bandage lightly above the bite to slow the venom’s spread.
• Take the person to the nearest hospital or call 108 ambulance services immediately.
II. Questioning and Hypothesis
4. What questions would you ask to know more about 108 Services?
• How quickly can 108 services respond to an emergency?
• What types of emergencies does 108 handle?
• What information should we provide while calling 108?
• How does the ambulance team provide first aid before reaching the hospital?
• Is the 108 service available 24/7 in all areas?
III. Experiments and Field-Based Observations
5. Visit an accident spot which is nearby. Find the causes of the accident and record your observations.
• Possible causes of accidents:
• Over-speeding
• Not following traffic signals
• Not wearing helmets or seat belts
• Walking or playing on the road carelessly
• Observations should include:
• The condition of the road (slippery, damaged, crowded)
• Actions of drivers and pedestrians before the accident
• Response time of emergency services
IV. Information Skills and Projects
6. Discuss the precautions to be taken while using fireworks on Diwali.
• Always burst crackers in an open space under adult supervision.
• Keep a bucket of water or sand nearby for emergencies.
• Wear cotton clothes to avoid catching fire.
• Avoid using fireworks near flammable materials.
• Do not relight a firework that did not burst the first time.
V. Drawing Pictures and Model Making
7. Draw a mind map showing precautions we take while traveling on a bus.

• Stand in a queue while boarding.
• Do not push others while getting on or off.
• Hold handrails for support.
• Avoid talking to the driver while he is driving.
• Never put hands or head outside the window.
VI. Appreciation
8. How do you appreciate the services of 108 and 104?
• 108 provides emergency medical services and helps save lives in accidents and medical crises.
• 104 provides medical advice over the phone, helping people access healthcare easily.
• These services are free and available 24/7, making them accessible to all.
• The ambulance staff and medical professionals work hard to save lives, so they deserve our respect and gratitude.

Let Us See an Amazing World
Andhra Pradesh | APSCERT
Home » Solutions » Class 5 » EVS Textbook Solutions » Chapter 8: Let Us See an Amazing World
Here are the answers to the “Improve Your Learning” section from the lesson Let Us See an Amazing World (Class 5 EVS)
I. Conceptual Understanding
1. Name the means of transport used to travel abroad.
• Airways: Aeroplanes, helicopters.
• Waterways: Ships, cargo ships, ferries.
2. Why do people travel abroad?
People travel abroad for various purposes, such as:
• Business: To trade and expand their business.
• Employment: To work in other countries.
• Education: To pursue higher studies.
• Tourism: To visit famous places.
• Sports: To participate in international games and championships.
3. Explain the terms import and export.
• Import: Buying goods from another country. Example: India imports Kiwi, Durian fruit, and Dragon fruit from other countries.
• Export: Selling goods to another country. Example: India exports mangoes, bananas, and pomegranates to foreign countries.
II. Questioning and Hypothesis
4. What type of questions would you like to ask your mother about the availability of apples in your village?
• Where do the apples in our village come from?
• Are apples grown in our village or imported from other places?
• How do apples reach the local market?
• Why do apples cost more than some other fruits?
• Are there any varieties of apples available?
III. Experiments and Field Observations
5. Visit a nearby paddy field and observe the process of exporting paddy, then prepare a report.
(Students should visit a local paddy field and observe the process. Example report:)
• Farmers grow paddy and harvest it when the grains are ready.
• After harvesting, the paddy is sent to mills for processing.
• Some of the paddy is kept for local use, while the extra paddy is packed in bags and sent to nearby cities.
• Large quantities of paddy are transported by trucks and ships to other countries for export.
6. Collect information about important tourism places around your village or town and prepare an album.
(Students should collect pictures and details of tourist spots. Example:)
• Tirupati Temple: Famous pilgrimage site.
• Lepakshi Temple: Historical site with ancient sculptures.
• Borra Caves: Beautiful natural caves.
• Lambasingi: Known as Andhra Kashmir for its cold climate.
IV. Drawing Pictures and Model Making
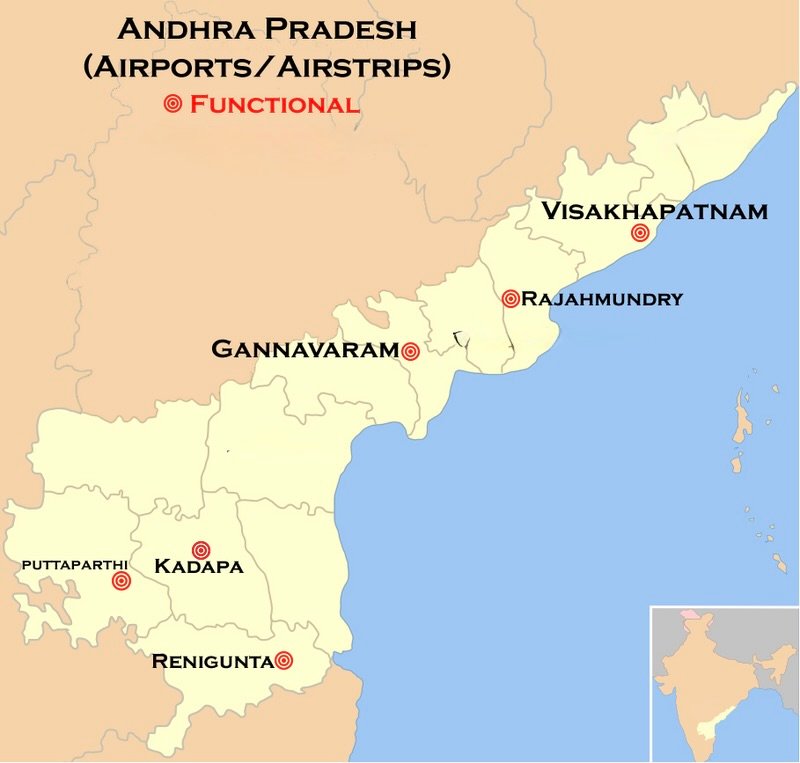
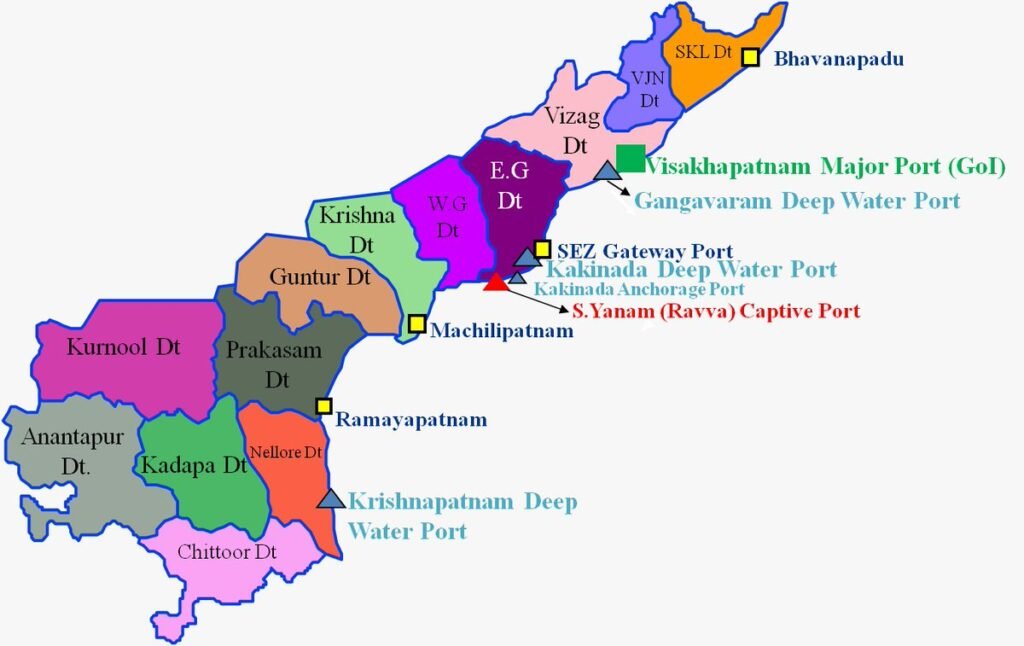
7. Identify and label different sea ports and airports on the map of Andhra Pradesh.
Major Airports in Andhra Pradesh:
• Visakhapatnam International Airport
• Vijayawada Airport
• Tirupati Airport
• Rajahmundry Airport

Major Sea Ports in Andhra Pradesh:
• Visakhapatnam Port
• Krishnapatnam Port
• Kakinada Port
• Gangavaram Port

V. Appreciation
8. What are the advantages of an airport?
• Fastest mode of transport for long distances.
• Helps people travel internationally for business, education, and tourism.
• Allows quick delivery of goods and cargo between countries.
• Supports economic growth by increasing trade and tourism.
• Provides employment opportunities for many people.
మా బడి e- మాస పత్రిక సంచిక-3: Dec-2024
Maa Badi e magazine-3-December-2024

Chapter 4: Know Our Organ Systems | Class 5 | EVS | AP SCERT
Andhra Pradesh | APSCERT
Home » Solutions » Class 5 » EVS Textbook Solutions » Chapter 4: Know Our Organ Systems
Based on Chapter 4, “Know our organ systems” from the Class 5 EVS textbook, here are the answers to the “Improve Your Learning” section.
Improve Your Learning
I. Conceptual Understanding
1. Name the parts of the circulatory system.
• The circulatory system consists of:
• Heart
• Blood
• Blood vessels (arteries and veins).
2. Which system is responsible for our body’s movement?
• The Skeletal System and Muscular System together support body movement.
3. What is inhalation and what is exhalation?
• Inhalation: The process of taking in oxygen-rich air into the lungs.
• Exhalation: The process of expelling carbon dioxide and water vapor from the lungs.
II. Questioning and Hypothesis
4. If you have a chance to meet a doctor (cardiologist), what type of questions would you ask about the heart?
• What is the role of the heart in the circulatory system?
• How can we keep our heart healthy?
• What causes heart diseases?
• How many times does the heart beat in a day?
• Why do athletes have slower heart rates?
III. Experiments and Field Observations
5. Place your hand on the heart and feel the heartbeat carefully. Run for some time and feel it again. Do you find any difference? Write the difference with reasons.
• Observation: The heartbeat increases after running.
• Reason: When we run, our muscles need more oxygen to produce energy. The heart beats faster to pump more oxygen-rich blood to the muscles and remove carbon dioxide efficiently.
IV. Information Skills and Projects
6. Visit a doctor or a nurse nearby and ask the functions of vital organs. Make a brief note.
• Brain: Controls all body functions and processes messages from sensory organs.
• Heart: Pumps blood, transporting oxygen and nutrients to the body.
• Lungs: Absorb oxygen and expel carbon dioxide during respiration.
• Kidneys: Filter blood and remove waste materials as urine.
• Liver: Helps in digestion and detoxifies harmful substances.
V. Drawing and Model Making
7. Draw the following on a chart. Label them and display them in the classroom:
• i) Digestive System: Include parts like mouth, oesophagus, stomach, small intestine, large intestine, rectum, and anus.

• ii) Excretory System: Include kidneys, ureters, bladder, and urethra.

VI. Appreciation
8. What amazes you in these body parts? Write down.
• The brain amazes me as it controls the entire body like a supercomputer.
• The heart pumps blood tirelessly, ensuring the survival of the body.
• The digestive system breaks down complex food into nutrients efficiently.
• The lungs provide oxygen, which is essential for energy.
• The kidneys filter impurities, keeping our blood clean.
The End

Chapter 3: Clothes We Wear | Class 5 | EVS | Textbook | Solutions | AP SCERT
Andhra Pradesh | APSCERT
Home » Solutions » Class 5 » EVS Textbook Solutions » Chapter 3: Clothes We Wear
Based on Chapter 3, “Clothes We Wear,” from the Class 5 EVS textbook, here are the answers to the “Improve Your Learning” section.
Improve Your Learning
I. Conceptual Understanding
1. Write a brief note on the uses of air?
- Air is essential for breathing and survival. It carries smells, produces sound, and helps in various daily activities like flying kites, drying clothes, and drinking liquids through straws. Wind power is used to generate electricity and lift water for cultivation.
2. Name the kind of clothes we wear in different seasons.
- Summer: Cotton clothes to keep cool.
- Winter: Woollen clothes to keep warm.
- Rainy Season: Raincoats and waterproof clothes to stay dry.
3.Write differences between natural and synthetic fibres.
- Natural Fibres: Obtained from plants and animals (e.g., cotton, wool, silk). They are eco-friendly and breathable.
- Synthetic Fibres: Made artificially using chemicals (e.g., polyester, nylon). They are durable and affordable.
II. Questioning and Hypothesis
4. Name the reasons why people use woollen clothes in the winter season.
Woollen clothes keep the body warm because wool traps heat and insulates against the cold. They are especially useful in cold climates.
III. Experiments and Field-Based Observations
5.Wash your dress with a detergent soap and write your experiences.
Experience: Washing clothes with detergent removes dirt and stains effectively. Dark-colored clothes should not be dried in direct sunlight to prevent fading. Proper washing and drying keep clothes clean and fresh.
IV. Information Skills and Projects
6. Collect pieces of cloth, classify them into natural fabrics and artificial fabrics, and paste them on the chart. Display the chart.
- Examples:
- Natural Fabrics: Cotton, Silk, Wool
- Artificial Fabrics: Polyester, Nylon, Rayon
V. Drawing Pictures and Model Making
7. Draw pictures of different types of dresses.
Students can draw sarees, dhotis, uniforms, and casual wear like jeans and T-shirts.
VI. Appreciation
8. Say what you like at a tailor’s shop
I like choosing the fabric for my clothes. Watching the tailor stitch the fabric into a perfect dress is fascinating. It feels exciting to see my ideas turn into reality.
The end

Chapter 2: Climate Change | Class 5 | EVS | Textbook Solutions
Andhra Pradesh | APSCERT
Home » Solutions » Class 5 » EVS Textbook Solutions » Chapter 2: Climate Change
Here are the answers to the “Improve Your Learning” section for the lesson “Climate Change”
I. Conceptual Understanding
1. What is climate?
• Climate refers to the weather conditions such as temperature and rainfall prevailing in an area over a long period.
2. What are the effects we face due to climate change?
• The effects of climate change include untimely rainfall, droughts, floods, melting of ice, rising sea levels, cyclones, tsunamis, and forest fires. It also impacts food production and causes the death of aquatic plants and animals.
3. What are the reasons for climate change?
• The main reasons for climate change are deforestation, pollution from industries and vehicles, overuse of natural resources, burning waste, and the excessive use of plastic and harmful chemicals.
II. Questioning and Hypothesis
4. In your village, people are suffering from drought. Can you guess the reasons?
• Drought could be due to a lack of rainfall caused by deforestation, climate change, overuse of groundwater, pollution, and improper agricultural practices.
III. Experiments and Field Observations
5. Observe the process used for disposing of garbage at your home and make a report.
• At home, garbage is segregated into wet waste (food leftovers, peels) and dry waste (plastic, paper). Wet waste is composted to make manure, while dry waste is sent for recycling or discarded. However, in some cases, improper disposal, such as burning or dumping, causes pollution.
IV. Information Skills and Projects
6. Collect information about students who are using steel water bottles instead of plastic water bottles.
• A survey at school shows that 60% of students use plastic bottles, while 40% have switched to steel bottles. The latter group prefers steel bottles for their durability, safety, and eco-friendliness, reducing plastic pollution.
V. Drawing and Model Making
7. Make a pen stand, flower vase, etc., by using a plastic water bottle.
• This activity involves cutting and decorating plastic bottles creatively to reuse them as pen stands, vases, or storage containers, promoting recycling.

VI. Appreciation
8. Prepare some slogans on ‘Save Environment.’
• “Plant Trees, Save Lives.”
• “Reduce, Reuse, Recycle.”
• “Say No to Plastic, Yes to Nature.”
• “Save Water, Save the Planet.”
• “Act Now, Save Tomorrow.”

Chapter 1: Migration of People
Class 5 | EVS | Textbook | Chapter 1: Migration of People | solutions
Andhra Pradesh | APSCERT
Home » Solutions » Class 5 » EVS Textbook Solutions » Chapter 1: Migration of People
Here are the answers to the “Improve Your Learning” section from the lesson “Chapter 1: Migration of People” for Class 5 EVS.
I. Conceptual Understanding
1. What is migration? Give some examples.
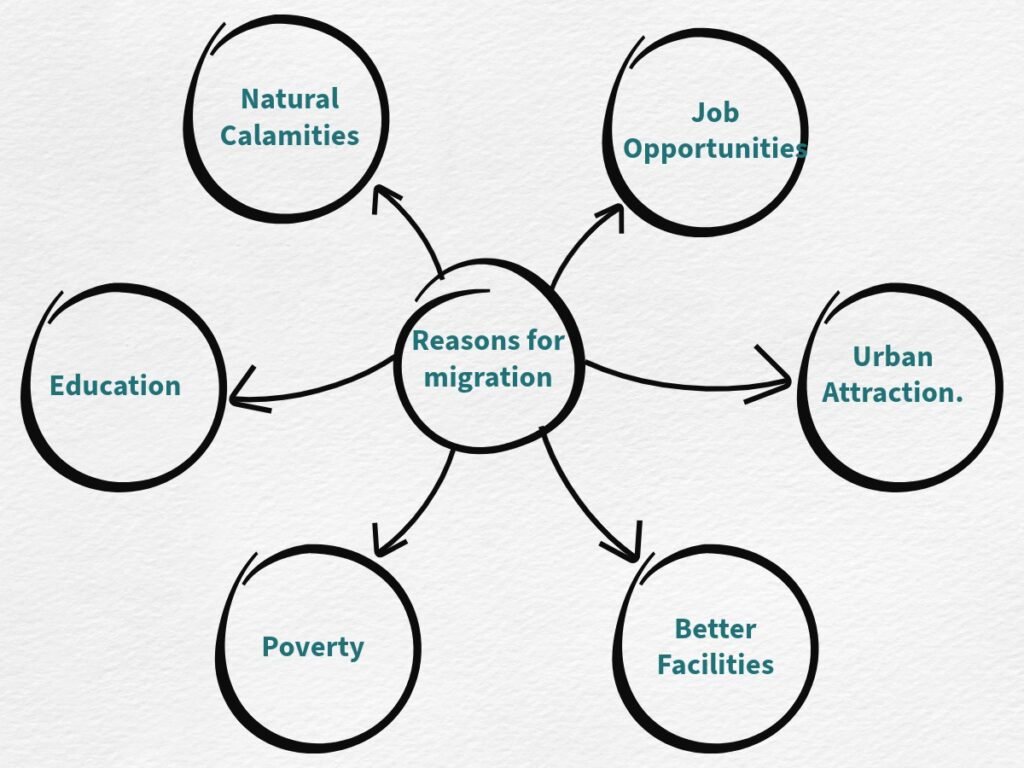
• Migration is the movement of people from one place to another in search of better livelihood, jobs, education, or due to natural calamities.
Examples:
• Praveen’s family migrated to Tirupati because of a job transfer.
• Kumari’s family moved to Chennai for better wages.
• Kondaiah’s family moved to Vijayawada after losing their home and crops in a cyclone.
2. What are the advantages and disadvantages of migration?
Advantages:
• Better job opportunities.
• Improved living conditions.
• Access to better education and facilities.
Disadvantages:
• Separation from relatives and friends.
• Adjustment to a new environment.
• Children may miss schooling.
• Increase in slums and overpopulation in urban areas.
3. Raju says that sometimes migration happens in our lives. Do you agree with this statement? Why?
• Yes, I agree. Migration can occur due to natural calamities, job transfers, poverty, or better opportunities. It helps people improve their lives but also comes with challenges.
II. Questioning and Hypothesis
4. If you meet a migrated family in your village, what type of questions would you ask them to find out the reasons for migration?
Examples of questions:
• Where did you live before coming here?
• Why did you decide to move?
• Did you face any problems in your previous place?
• What do you like about this new place?
• Has migration improved your living conditions?
III. Experiments and Field Observations
5. Observe migrated families in your village/town because of COVID-19 and record their experiences.
• Many families moved back to their villages as they lost jobs in cities.
• Children missed school and struggled with online education.
• Families relied on government schemes for food and support.
IV. Information Skills and Project Work
6. Find out the reasons for the drop-outs in your surroundings:
S.No. Name of the Student Reasons 1 Ravi Helping parents in their work 2 Lakshmi Financial problems at home 3 Kiran Family migrated to another village V. Drawing Pictures and Model Making
7. Draw a mind map showing the reasons for migration.

VI. Appreciation
8. Suresh is going to work with his father. He stopped going to school. How do you motivate him to rejoin school?
Suresh, school is very important for your future. If you study well, you can get a good job and help your family in a better way. You can still help your father after school hours.
Many successful people also faced struggles but continued their education. Your teachers and friends are waiting for you! If there are any problems, we can find solutions together. Education will give you a bright future! 😊✨
class 4 practice tests
- Telugu
- English
- Maths
- evs
Telugu
English
Maths
- chapter: 1
- chapter: 2
- chapter: 3
- chapter: 4
- chapter: 5
- chapter: 6
- chapter:7: professions and service
- chapter: 8
- chapter: 9
- chapter: 10
- chapter: 11